Turns APIs described by OpenAPI specifications (OAS) into GraphQL interfaces.
An example application exposing GitHub's public REST-like API via OASGraph can be found here (source code).
Our research paper, "Generating GraphQL-Wrappers for REST(-like) APIs", describes the challenges of building OASGraph and evaluates it against 959 publicly available OAS (and successful creating GraphQL interfaces for 89.5% of those OAS). It can be found here.
-
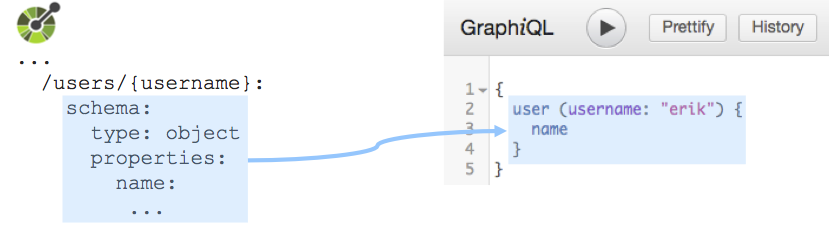
Data-centric The GraphQL interface is created around the data definitions in the given OAS, not around the endpoints, leading to a natural use of GraphQL.
-
Nested data Links defined in the OAS are used to compose data definitions. Furthermore, hierarchical path structures can be used to nest data via the
addSubOperationsoption.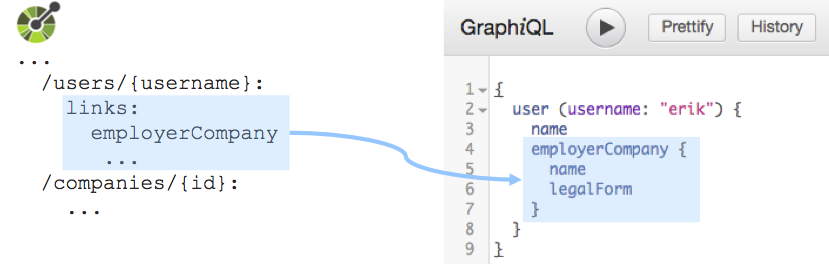
-
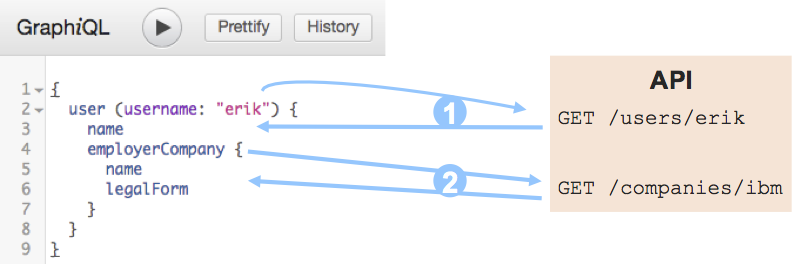
Automatic query resolution Automatically generated resolvers translate (nested) GraphQL queries to API requests. Request results are translated back to GraphQL responses.
-
Mutations Non-safe, non-idempotent API operations (e.g.,
POST,PUT,DELETE) are translated to GraphQL mutations. Input payload is type-checked.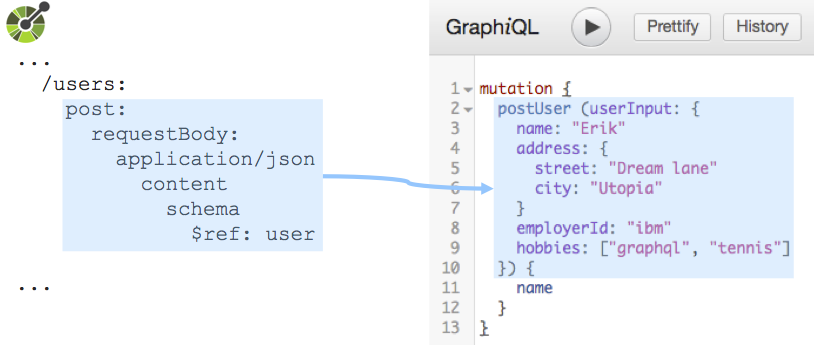
-
Authentication OASGraph currently supports authentication via API Key and basic auth. OASGraph wraps secured endpoints into a
viewer, which takes the API key / credentials as input.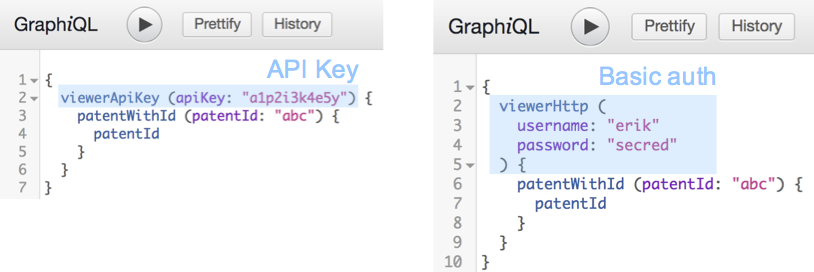
-
API Sanitation Parts of an API that not compatible with GraphQL are automatically sanitized. For example, API parameters and data definition names with unsupported characters (e.g.,
-,.,,,:,;...) are removed. GraphQL queries are desanitized to correctly invoke the REST API and the responses are resanitized to create GraphQL-compliant results.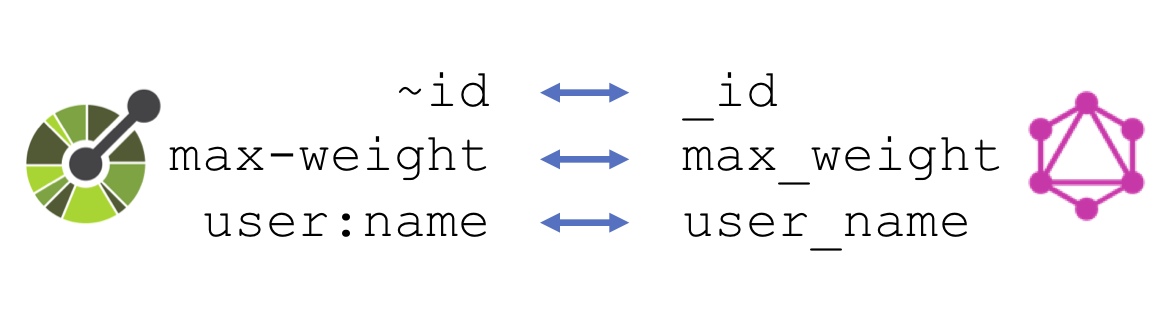
-
Custom request options Provide headers and query parameters to send with every API request. This allows, for example, to handle authentication or tag requests from GraphQL.
-
Swagger and OpenAPI 3 support OASGraph can handle both Swagger (OpenAPI specification 2.0) as well as OpenAPI specification 3.
Install this package. Make sure to also have installed GraphQL.js (using npm i graphql), as it is a required peer-dependency. Then, simply pass it an OpenAPI Specification 3.0. The library returns a promise that resolves on an object containing the schema:
const OASGraph = require('oasgraph') // use real name here
let oas = require('./fixtures/example_oas.json') // or other means of obtaining the OAS
OASGraph.createGraphQlSchema(oas)
.then(({schema}) => {
// do something with the schema
})
.catch(err => {
// handle errors when creating the schema
})You can then use the generated schema, for example to be served using Express.js:
const express = require('express')
const graphqlHTTP = require('express-graphql')
const OASGraph = require('oasgraph') // use real name here
const app = express()
OASGraph.createGraphQlSchema(oas)
.then(({schema}) => {
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema,
graphiql: true
}))
app.listen(3001)
})
.catch(err => {
// handle errors when creating the schema
})Alternatively, use the CLI tool.
Usage: oasgraph <OAS JSON file path>
Please note that the CLI tool is mainly used for quick testing and does not offer all the features that createGraphQlSchema(oas, options) does.
OASGraph allows to define an optional options object:
OASGraph.createGraphQLSchema(oas, options)The following options can be set:
-
strict(type:boolean, default:false): OASGraph generally tries to produce a working GraphQL interface for a given OAS. If OASGraph cannot fully translate a given OAS (e.g., because data schema definitions are incomplete or there are name collusions that cannot be resolved), OASGraph will per default degrade gracefully and produce a partly working GraphQL interface. OASGraph will log warnings (given logging is enabled). If OASGraph operates instrictmode, however, it will throw if it cannot create a GraphQL interface matching the given OAS perfectly. -
headers(type:object, default:{}): Headers to be sent in every request. Parameters defined in the OpenAPI Specification to set these headers will be ignored by OASGraph. -
qs(type:object, default:{}): Query parameters to be sent in every request. Parameters defined in the OpenAPI Specification to set these query parameters will be ignored by OASGraph. -
viewer(type:boolean, default:true): The viewer object types (i.e. QueryViewer and MutationViewer) are artificial constructs that allow a user to pass authentication credentials to OASGraph. Unfortunately, they are bulky and do not provide an accurate representation of the API. Depending on the API, it may be possible to send all your credentials through the header option, so if you would like to authenticate without the OASGraph-generated viewer object types, you can set the viewer option to false. -
tokenJSONpath(type:string, default:undefined): Used to pass the JSONPath of the OAuth token in the GraphQL context. To see more details, click here. -
addSubOperations(type:boolean, default:false): When true, OASGraph will nestGEToperations based on their path hierarchy in the given OAS. E.g., when the OAS contains two paths/users/{id}and/users/{id}/friends, OASGraph will makefriendsqueryable from withinuser. Note: This may cause problems when resolving GraphQL types in certain contexts, where the required variables are not available.
Consider this example of passing options:
OASGraph.createGraphQLSchema(oas, {
headers: {
authorization: 'asfl3032lkj2' // send authorization header in every request
'x-origin': 'GraphQL' // send header to identify requests made via GraphQL
},
qs: {
limit: 30 // send limit query string in every request
},
addSubOperations: false
})Per default, OASGraph will wrap API requests that need authentication in corresponding viewers, which allow the user to pass required credentials. OASGraph currently supports viewers for basic authentication and API keys. For example, a query using an API key viewer is:
{
viewerApiKey (apiKey: "api_key_here") {
... // query for authenticated data here
}
}OASGraph uses dedicated viewers for mutations. For example, a mutation using a basic authentication viewer is:
mutation {
mutationViewerBasic (username: "user", password: "secret") {
... // mutate authenticated data here
}
}OASGraph further provides anyAuth viewers (for queries and mutations), which allow the user to simultaneously provide information for multiple authentication mechanisms. AnyAuth viewers allow OASGraph to resolve nested queries and mutations that encompass API requests with different authentication mechanisms. For example, consider the following query:
{
viewerAnyAuth (
exampleApiKeyProtocol: {apiKey: "a1p2i3k4e5y"}
exampleBasicProtocol: {
username: "erik"
password: "secret"
}
) {
patentWithId (patentId: "test") { // requires "exampleApiKeyProtocol"
patentId
inventor { // requires "exampleBasicProtocol"
name
}
}
}
}OASGraph now supports OAuth 2.0!
Because OASGraph is a library, it cannot make the callbacks that OAuth requires by itself. Instead, the user must take care of the callback. After the user has obtained the OAuth token from the callback, simply pass the token, specifically the path of the token, to OASGraph through the tokenJSONpath option.
To see an example of how this would work, click here!
To test OASGraph, first make sure the example API server is running:
npm run apiThen, run tests:
npm testOASGraph can be applied to all OAS contained in APIs.guru OpenAPI repository. Load APIs.guru specifications into the /tmp folder:
npm run guru-loadThen, run tests:
npm run guru-test <number of APIs to test at most>OASGraph provides multiple levels of logging, which can be controlled by a DEBUG environment variable. You can enable these levels using:
DEBUG=level_1,level_2 node app-using-oasgraph.jsThe following logging levels are supported:
preprocessing: Logs information about preprocessing the OAS to GraphQL.translation: Logs information about translating an OAS to GraphQL.http: Logs information about the HTTP requests made to the API.
OASGraph is written in TypeScript. All source code is contained in the src folder. Use npm run build or npm test to transpile the source files into the final library in the lib folder. Entry-point for the library is index.js in lib.
-
swagger-to-graphql turns a given Swagger (OpenAPI Specification 2.0) into a GraphQL interface, which resolves against the original API. GraphQL schema is based on endpoints, not on data definitions. No links are considered.
-
json-to-graphql turns given JSON objects / arrays into a GraphQL schema.
resolvefunctions need to be provided by the user. -
StackOverflow discussion points to the above projects.