DSA stands for "Data Structures and Algorithms." In computer science and programming, data structures refer to the way data is organized and stored in a computer's memory, while algorithms are a set of step-by-step instructions for solving a particular problem or task.
Data structures and algorithms are an essential part of computer science and programming. They help programmers create efficient and effective software by organizing data in ways that make it easy to manipulate and retrieve, and by providing efficient algorithms for performing common operations on that data.
For example, some common data structures include arrays, linked lists, trees, graphs, and hash tables. Algorithms can be used to search and sort data, traverse trees and graphs, and perform many other operations on data structures.
Knowing data structures and algorithms can help you write more efficient and effective code, and is an important skill for any programmer to have.
- A data structure is not only used for organizing the data. It is also used for processing, retrieving, and storing data. There are different basic and advanced types of data structures that are used in almost every program or software system that has been developed. So we must have good knowledge about data structures.
-
-
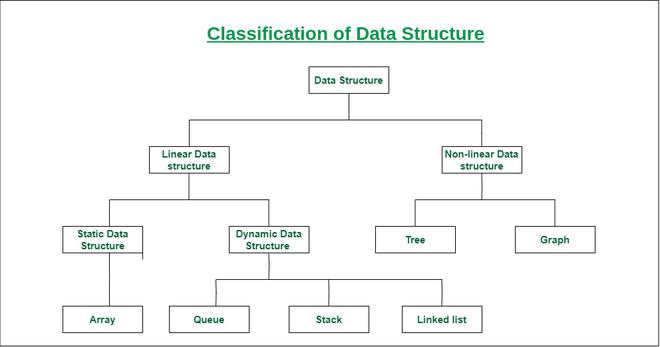
Linear data structure: Data structure in which data elements are arranged sequentially or linearly, where each element is attached to its previous and next adjacent elements, is called a linear data structure. Examples of linear data structures are array, stack, queue, linked list, etc.
- Static data structure: Static data structure has a fixed memory size. It is easier to access the elements in a static data structure. An example of this data structure is an array.
- Dynamic data structure: In dynamic data structure, the size is not fixed. It can be randomly updated during the runtime which may be considered efficient concerning the memory (space) complexity of the code. Examples of this data structure are queue, stack, etc.
-
Non-linear data structure: Data structures where data elements are not placed sequentially or linearly are called non-linear data structures. In a non-linear data structure, we can’t traverse all the elements in a single run only. Examples of non-linear data structures are trees and graphs.